Find K smallest and largest values and its indices in a numpy array
To find the maximum and minimum value in an array you can use numpy argmax and argmin function
These two functions( argmax and argmin ) returns the indices of the maximum value along an axis
However, if you are interested to find out N smallest or largest elements in an array then you can use numpy partition and argpartition functions
In this post we are going to discuss how numpy partition and argpartition works and how to use it for finding N small and large values and their indices
Numpy Partition
It return a partitioned copy of array
Perform an indirect partition along the given axis using the algorithm specified by the kind keyword. It returns an array of indices of the same shape as a that index data along the given axis in partitioned order
Basically it gives the indices of the N smallest and largest values along the given axis of a numpy array
Find N smallest values in a Numpy array
Create a 1D array
import numpy as np
arr=np.random.randint(0,100,size=10)
Output:
array([69, 38, 60, 91, 4, 81, 54, 45, 13, 95])
Now we are interested to find 4 smallest values in this array
We will use numpy partition to get those 4 smallest values
np.partition(arr,4)
Output:
array([38, 45, 4, 13, 54, 60, 69, 81, 91, 95])
Let’s understand the output of numpy partition
Original Array:

Now we want to find 4 smallest values in this array, so we will partition the original array at 4th position, Which will look like this

Now move the smallest values on the left partition and larger value on the right side as it would be in a sorted array
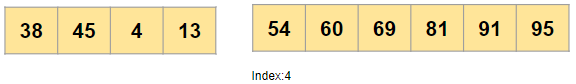
Note: As mentioned in the document the ordering of the elements in the two partitions is undefined i.e. it can be any arbitrary order
Now you will merge these two partition and that will be the output of numpy partition
So if you want to get the first 4 smallest values from the original array then
np.partition(arr,4)[:4]
Output:
array([38, 45, 4, 13])
Find N Largest values in a Numpy array
To find 4 largest values from the above original array, Just pass a -4 value in numpy partition function
np.partition(arr,-4)[-4:]
The below output gives you 4 largest values from the original array
Output:
array([69, 81, 91, 95])
In the next section we will see how to find the indices of the N smallest and largest values in an array
Numpy Argpartition
As per the documentation
Perform an indirect partition along the given axis using the algorithm specified by the kind keyword. It returns an array of indices of the same shape as a that index data along the given axis in partitioned order
Basically it gives the indices of the N smallest and largest values along the given axis of a numpy array
Find indices of N smallest values in a Numpy array
Let’s take the same original array
arr= np.array([69, 38, 60, 91, 4, 81, 54, 45, 13, 95])
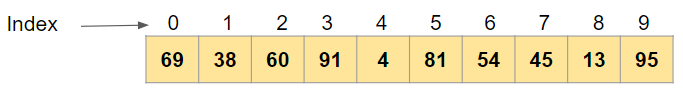
Now this time we wanted to find the indices of the 4 smallest values in this array
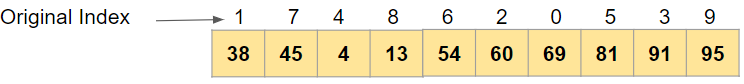
np.argpartition(arr,4)
The output is indices of all the array elements arranged in such a way that 4 smallest value indices are left of index=4 and all large value indices are on right
Output:
array([1, 7, 4, 8, 6, 2, 0, 5, 3, 9], dtype=int64)
Now if you are interested to want the values of 4 smallest values
arr[np.argpartition(arr,4)[:4]]
Ouptut:
array([38, 45, 4, 13])
Find indices of N largest values in a Numpy array
Similarly for finding the 4 largest values in the original array using numpy argpartition we have to pass a negative value
np.argpartition(arr,-4)
Output:
array([6, 4, 2, 8, 1, 7, 0, 5, 3, 9], dtype=int64)
Now we will find the values of those 4 largest values
arr[np.argpartition(arr,-4)[-4:]]
Output:
array([69, 81, 91, 95])