Concatenating arrays in Numpy
We will be discussing about merging numpy arrays and different functions that are available in the toolbox to perform this job
Did you ever thought why we have Append,Concatenate, vstack, hstack etc. functions when all does the same job
Lets start with difference between numpy concatenate and append
Numpy Concatenate vs Append
numpy append uses concatenate under the hood
Append is used for appending the values at the end of the array provided the arrays are of the same shape
Whereas Concatenate is used for joining the sequence of array along an existing axis
a= np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
b = np.array([7,8,9])
array([7, 8, 9])
Can you append array b to array a?
Shape of array a: (2,3) and array b: (3,)
No, You cannot append b to a, numpy append will throw a value error
ValueError: all the input arrays must have same number of dimensions, but the array at index 0 has 2 dimension(s) and the array at index 1 has 1 dimension(s)
So what you have to do to append array b to a?
Change the shape of array b from (3,) to (1,3)
b = np.array([[7,8,9]])
array([[7, 8, 9]])
Now try appending b to a and it will work
np.append(a,b, axis=0)
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]])
Numpy concatenate 1D arrays
Take two one dimensional arrays and concatenate it as a array sequence

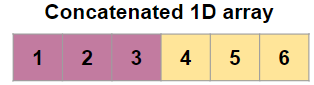
So you have to pass [a,b] inside the concatenate function because concatenate function is used to join sequence of arrays
import numpy
a = numpy.array([1, 2, 3])
b = numpy.array([5, 6])
numpy.concatenate(a, b)
Output:
array([1, 2, 3, 5, 6])
numpy r_
We can also concatenate these two 1D arrays using numpy r_ . It’s a simple way to build up arrays quickly
it returns a concatenated ndarray or matrix
np.r_[a,b]
numpy stack
you can also use stack to join sequence of arrays. Just make sure both the 1D arrays are of the same shape
a = np.array([1, 2,3])
b = np.array([5, 6,7])
np.stack([a,b]).reshape(-1)
array([1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7])
You have to reshape the resultant array to flatten it and get a 1D array
numpy hstack
It Stack arrays in sequence horizontally, So if two 1D arrays are given then it flatten it to a single 1D
a = np.array((1,2,3))
b = np.array((5,6))
np.hstack((a,b))
array([1, 2, 3, 5, 6])
Numpy Concatenate 2D arrays
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
b = np.array([[5, 6]])
a:
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
b:
array([[5, 6]])
Now, Concatenate these two arrays along the rows
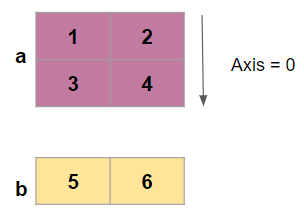
Look at the axis value it is passed as 0 to merge along the rows
np.concatenate((a, b), axis=0)
Output:
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6]])
numpy vstack
It Stack arrays in sequence vertically i.e row wise
You can concatenate the above 2D arrays using vstack and will get the same result as concatenate with axis =0
np.vstack((a,b))
Let’s merge the above two arrays along the axis =1
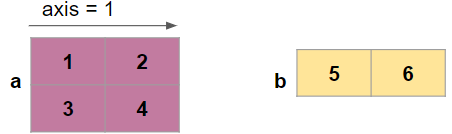
np.concatenate((a, b), axis=1)
Output: ValueError: all the input array dimensions for the concatenation axis must match exactly
But why it’s throwing an error, because both the arrays doesn’t have the same dimensions along 0 to concatenate
So how do we change the dimension for this concatenation
Transpose the array B and then concatenate along axis = 1
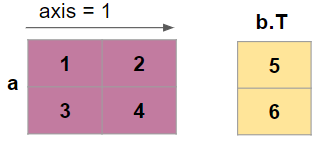
np.concatenate((a, b.T), axis=1)
array([[1, 2, 5],
[3, 4, 6]])
if we give axis as None then it will flatten the 2D arrays and convert to 1D array
np.concatenate((a, b), axis=None)
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
Numpy Concatenate 1D array to 2D array
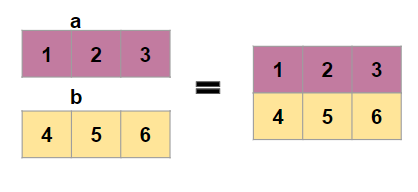
First create two 1D arrays
a = np.array((1,2,3))
b = np.array((2,3,4))
Now we will concatenate this along rows to get a 2D array
Using numpy vstack
np.vstack((a,b))
array([[1, 2, 3],
[2, 3, 4]])
Using numpy concatenate
For this you have to reshape the original arrays
np.concatenate([a.reshape(1,3),b.reshape(1,3)])
array([[1, 2, 3],
[2, 3, 4]])
if you want to concatenate these two arrays along axis = 1
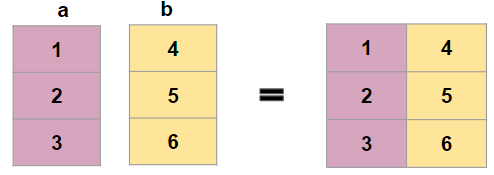
Using stack
a = np.array((1,2,3))
b = np.array((4,5,6))
np.stack((a,b),axis=1)
array([[1, 4],
[2, 5],
[3, 6]])
Using Concatenate
np.concatenate((a.reshape(3,1),b.reshape(3,1)),axis = 1)
Using hstack
np.hstack([a.reshape(3,1),b.reshape(3,1)])
Numpy Stack 2d Arrays

a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
b = np.array([[5, 6],[7,8]])
a:
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
b:
array([[5, 6],
[7, 8]])
np.stack((a,b))
array([[[1, 2],
[3, 4]],
[[5, 6],
[7, 8]]])
Stack along axis = 1
np.stack((a,b),axis=1)
array([[[1, 2],
[5, 6]],
[[3, 4],
[7, 8]]])
Stack along axis = -1 i.e. last axis
np.stack((a,b),axis=-1)
array([[[1, 5],
[2, 6]],
[[3, 7],
[4, 8]]])